How 3D Printing is Revolutionizing Manufacturing: Innovations, Benefits & Future Trends
Beyond Prototypes: How 3D Printing is Revolutionizing Manufacturing
Introduction:
3D printing, or additive manufacturing, has progressed far beyond its early days as a tool for creating prototypes. Today, this cutting-edge technology is driving innovation across industries like healthcare, aerospace, automotive, and more. But what makes 3D printing such a game-changer for manufacturing? Let’s delve into its transformative impact.
What is 3D Printing?
At its core, 3D printing is a process of creating three-dimensional objects layer by layer using digital design files. Unlike traditional manufacturing, which often involves cutting or molding material, 3D printing adds material only where it is needed. Popular methods include Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM), Stereolithography (SLA), and Selective Laser Sintering (SLS). Each technique offers unique advantages depending on the materials and applications.
Applications of 3D Printing in Manufacturing
- Custom Tooling:
Manufacturers are increasingly turning to 3D printing to produce custom
tools and fixtures quickly and at a lower cost compared to conventional
methods. This accelerates production timelines and reduces expenses.
- On-Demand Spare Parts:
Downtime in production lines can be costly. With 3D printing, companies
can produce spare parts on-site as needed, eliminating delays caused by
shipping and inventory shortages.
- Mass Customization:
3D printing enables the creation of highly customized products tailored to
individual needs. Examples include prosthetics in healthcare, uniquely
designed fashion pieces, and bespoke automotive components.
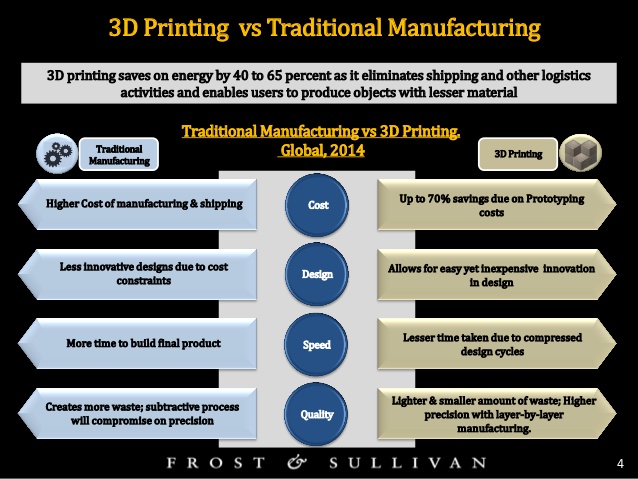
Benefits of 3D Printing in Manufacturing
- Reduced Material Waste: Unlike traditional subtractive methods, which remove
material to shape a product, 3D printing only uses the material required
to build the object, minimizing waste.
- Faster Production Cycles: By eliminating the need for complex tooling or molds,
3D printing significantly reduces the time it takes to move from design to
final product.
- Cost Efficiency:
Additive manufacturing lowers costs by reducing material usage,
eliminating the need for expensive molds, and simplifying logistics.
Challenges of Scaling 3D Printing
Despite its advantages, 3D printing
faces certain challenges when it comes to scaling for mass production. These
include:
- Material Limitations:
Many 3D printing materials lack the strength and durability required for
some industrial applications.
- Production Speed:
While 3D printing excels in customization, it is generally slower than
traditional manufacturing methods for large-scale production.
- Post-Processing Requirements: Many 3D-printed parts require additional finishing
steps, such as sanding or coating, which can add time and cost.
Conclusion
3D printing is undoubtedly reshaping
the future of manufacturing by offering unparalleled flexibility, efficiency,
and innovation. As the technology continues to advance, its applications will
expand further, making it an integral part of modern production processes.
Explore More
- Watch in Action:
https://youtu.be/vsIGAQU72Ys Discover
how leading companies are using 3D printing to revolutionize their
workflows.
- Learn More: https://www.digikey.com/Site/Global/Layouts/DownloadPdf.ashx?pdfUrl=67DB2D0FAC3F48AF9CEC3AD96ADA6E12 Dive into a comprehensive guide on the role of 3D printing in industrial
manufacturing.









Post a Comment