Russia’s Revolutionary Plasma Engine: The Future of Deep Space Travel
Russia’s Revolutionary Plasma Engine: The Future of Deep Space Travel
Space travel has always been constrained by long transit times, with missions to Mars taking around seven months using conventional rockets. But now, a groundbreaking plasma propulsion system developed by Russian scientists could cut that travel time down to just 30 days, an astonishing leap forward for space exploration
This next-generation plasma engine is capable of accelerating charged particles at speeds of up to 100 km/s (62 miles/s), making it one of the most efficient propulsion systems ever conceived. In this post, we’ll explore the science behind plasma propulsion, its potential impact on space travel, and what this means for future missions.
Understanding Plasma Propulsion: How Does It Work?
 |
| engineerine.com |
1.
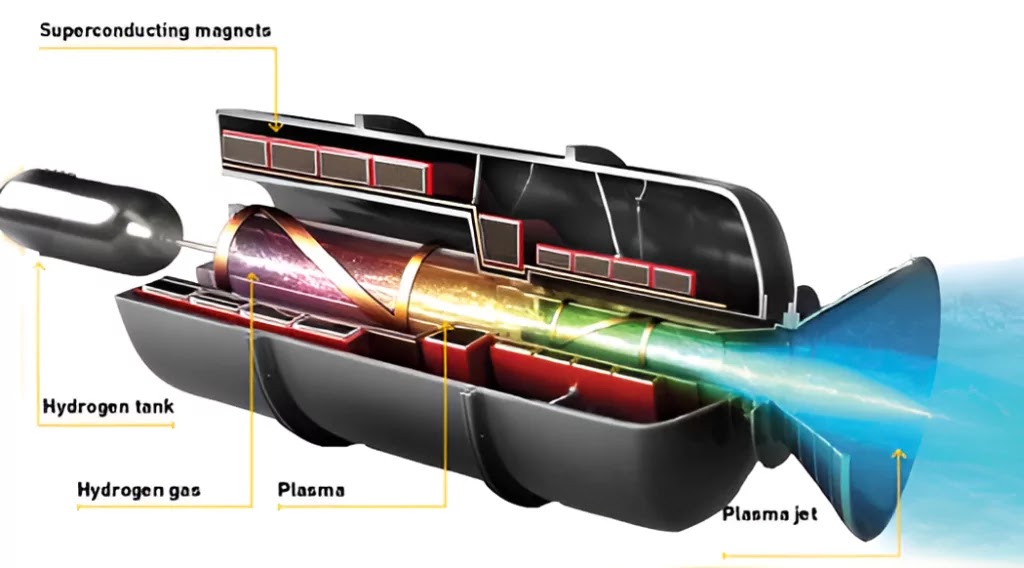
Plasma-Based Propulsion: The Future of Space Travel
A plasma rocket engine
operates on a completely different principle than chemical propulsion. Instead
of relying on combustion, it uses electrically charged particles (plasma)
accelerated by magnetic fields to generate thrust. Here’s how it works:
- Ionization:
The engine generates plasma by stripping electrons from atoms (typically
hydrogen).
- Magnetic Acceleration: The charged plasma particles are accelerated by a
strong magnetic field.
- Thrust Generation:
The high-speed plasma is expelled, propelling the spacecraft forward
efficiently.
This process allows for continuous
acceleration over long distances, making deep-space missions faster and
more practical than ever.
Most spacecraft today rely on chemical propulsion, which works by burning fuel to expel gases and generate thrust. While effective for launches from Earth, chemical rockets have significant drawbacks:
- Fuel consumption is extremely high, limiting their range.
- Travel times for deep-space missions are long, making interstellar exploration impractical.
- Heavy fuel loads increase spacecraft weight, reducing efficiency.
Plasma propulsion offers a far more sustainable and efficient alternative, enabling long-duration missions without the excessive fuel demands of traditional rockets.
The
Power of Russia’s New Plasma Engine
 |
| Image: Rosatom |
1.
Key Specifications
The newly developed Russian plasma
engine boasts some impressive technical features:
|
Feature |
Plasma
Engine Capability |
|
Propulsion Type |
Plasma-based electric propulsion |
|
Fuel Source |
Hydrogen |
|
Maximum Particle Speed |
100 km/s (62 miles/s) |
|
Power Output |
300 kW |
|
Projected Mars Travel Time |
30 days (instead of 7 months!) |
One of the most exciting aspects of
this technology is its ability to dramatically cut interplanetary travel
times. A mission to Mars using traditional chemical propulsion takes
approximately 7 months, but with plasma propulsion, this could be
reduced to just 30 days!
2.
Advantages Over Conventional Rocket Engines
Russia’s plasma engine offers
several key advantages compared to traditional propulsion systems:
· § Much Higher Speeds – Plasma particles move at 100 km/s, far exceeding the capabilities of conventional rockets.
· § Greater Fuel Efficiency – Plasma engines use electricity instead of large amounts of propellant, reducing spacecraft weight and fuel costs.
· § Ideal for Deep-Space Travel – Enables missions beyond Mars to Jupiter, Saturn, and potentially interstellar destinations.
· § Sustainable Technology – Hydrogen is an abundant fuel source, making this propulsion method environmentally and economically viable.
With these benefits, plasma propulsion could become the foundation for humanity’s journey beyond Earth’s orbit, setting the stage for interplanetary colonization and asteroid mining missions.
Challenges
& Future Development
Despite its potential, plasma
propulsion technology still faces several challenges before it can be
fully integrated into space missions:
§ Energy Requirements: Plasma engines require large amounts of electrical power, so spacecraft must be equipped with advanced nuclear reactors or solar power sources.
§ System Stability: Plasma acceleration must be precisely controlled to maintain thrust efficiency across long distances.
§
Long-Term Durability: Scientists are
working on solutions to ensure plasma engines can function reliably for
years in deep space conditions.
Russian engineers are actively
working on testing prototype models and improving efficiency to
overcome these challenges. As the technology matures, plasma propulsion may
soon become the gold standard for interplanetary and interstellar
exploration.
The Future of Space Travel
1.
Expanding Human Presence Beyond Earth
If plasma propulsion proves
successful, it could enable groundbreaking space projects, including:
· · Permanent Lunar Bases – Plasma engines could make reliable lunar transportation a reality.
· · Mars Colonization – Reduced travel time would make sustained human presence on Mars more viable.
· · Asteroid Mining Missions – Faster, more efficient spacecraft could enable mining operations on asteroids rich in valuable metals.
2.
Could We Witness Interstellar Travel?
One of the biggest questions
surrounding plasma propulsion is whether it could enable interstellar
missions. Plasma engines could, in theory, make travel beyond our solar
system feasible, though it would require advancements in nuclear-powered
spacecraft to sustain acceleration.
With global space agencies pushing the
boundaries of technology, we may be entering an era where interstellar
voyages are no longer just science fiction!
Conclusion:
A New Era for Space Exploration
Russia’s plasma electric rocket
engine is a revolutionary step forward in propulsion technology,
offering high efficiency, rapid travel times, and potential for
deep-space missions. If successfully implemented, this engine could pave
the way for Mars colonies, lunar bases, and even interstellar exploration.
With advancements accelerating, one
thing is clear: the future of space travel is closer than we ever imagined.








Post a Comment